Class 12 Chemistry - Chapter Surface Chemistry NCERT Solutions | What are micelles? Give an example of a
What are micelles? Give an example of a micellers system.
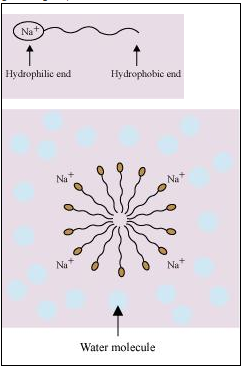
Micelles formation is done by substances soaps and detergents when dissolved in water.The Molecules of such substances contain a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic part. when present in water, these substances arrange themselves in spherical structure in such a manner that their hydrophobic parts are present towards the centre, while the hydrophilic parts are pointing towards outside (as shown in the given figure). This is known as micelles formation.
More Questions From Class 12 Chemistry - Chapter Surface Chemistry
- Q:-
Explain what is observed
(i) When a beam of light is passed through a colloidal sol.
(ii) An electrolyte, NaCl is added to hydrated ferric oxide sol.
(iii) Electric current is passed through a colloidal sol?
- Q:-
Why is adsorption always exothermic?
- Q:-
What do you mean by activity and selectivity of catalysts?
- Q:-
What modification can you suggest in the Hardy-Schulze law?
- Q:-
Explain the following terms:
(i) Electrophoresis
(ii) Coagulation
(iii) Dialysis
(iv) Tyndall effect.
- Q:-
What is an adsorption isotherm? Describe Freundlich adsorption isotherm.
- Q:-
Explain the terms with suitable examples:
(i) Alcosol
(ii) Aerosol
(iii) Hydrosol
- Q:-
How are colloids classified on the basis of
(i) Physical states of components
(ii) Nature of dispersion medium and
(iii) Interaction between dispersed phase and dispersion medium?
- Q:-
Discuss the effect of pressure and temperature on the adsorption of gases on solids.
- Q:-
Why does physisorption decrease with the increase of temperature
Popular Questions of Class 12 Chemistry
- Q:-
For the reaction R → P, the concentration of a reactant changes from 0.03 M to 0.02 M in 25 minutes. Calculate the average rate of reaction using units of time both in minutes and seconds.
- Q:-
Write the formulas for the following coordination compounds:
(i) Tetraamminediaquacobalt (III) chloride
(ii) Potassium tetracyanonickelate(II)
(iii) Tris(ethane-1,2-diamine) chromium(III) chloride
(iv) Amminebromidochloridonitrito-N-platinate(II)
(v) Dichloridobis(ethane-1,2-diamine)platinum(IV) nitrate
(vi) Iron(III) hexacyanoferrate(II)
- Q:-
(i) Write structures of different isomeric amines corresponding to the molecular formula, C4H11N
(ii) Write IUPAC names of all the isomers.
(iii) What type of isomerism is exhibited by different pairs of amines?
- Q:-
Why are solids rigid?
- Q:-
Write the structures of the following compounds.
(i) α-Methoxypropionaldehyde
(ii) 3-Hydroxybutanal
(iii) 2-Hydroxycyclopentane carbaldehyde
(iv) 4-Oxopentanal
(v) Di-sec-butyl ketone
(vi) 4-Fluoroacetophenone
- Q:-
Which of the ores mentioned in Table 6.1 can be concentrated by magnetic separation method?
- Q:-
Why are pentahalides more covalent than trihalides?
- Q:-
Silver atom has completely filled d orbitals (4d10) in its ground state. How can you say that it is a transition element?
- Q:-
Glucose or sucrose are soluble in water but cyclohexane or benzene (simple six membered ring compounds) are insoluble in water. Explain.
- Q:-
Write structures of the following compounds:
(i) 2-Chloro-3-methylpentane
(ii) 1-Chloro-4-ethylcyclohexane
(iii) 4-tert. Butyl-3-iodoheptane
(iv) 1,4-Dibromobut-2-ene
(v) 1-Bromo-4-sec. butyl-2-methylbenzene
Recently Viewed Questions of Class 12 Chemistry
- Q:-
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds:
(i) CH3CH(Cl)CH(Br)CH3
(ii) CHF2CBrClF
(iii) ClCH2C≡CCH2Br
(iv) (CCl3)3CCl
(v) CH3C(p-ClC6H4)2CH(Br)CH3
(vi) (CH3)3CCH=CClC6H4I-p
- Q:-
Concentrated nitric acid used in laboratory work is 68% nitric acid by mass in aqueous solution. What should be the molarity of such a sample of the acid if the density of the solution is 1.504 g mL-1?
- Q:-
Vapour pressure of pure acetone and chloroform at 328 K are 741.8 mm Hg and 632.8 mm Hg respectively. Assuming that they form ideal solution over the entire range of composition, plot ptotal' pchloroform' and pacetoneas a function of xacetone. The experimental data observed for different compositions of mixture is.
100 ×xacetone
0 11.8 23.4 36.0 50.8 58.2 64.5 72.1 pacetone /mm Hg
0 54.9 110.1 202.4 322.7 405.9 454.1 521.1 pchloroform/mm Hg
632.8 548.1 469.4 359.7 257.7 193.6 161.2 120.7 - Q:-
The value of ΔfGø for formation of Cr2O3 is - 540 kJmol-1 and that of Al2 O3 is - 827 kJmol-1. Is the reduction of Cr2O3 possible with Al?
- Q:-
Arrange the following in the order of property indicated for each set:
(i) F2, Cl2, Br2, I2- increasing bond dissociation enthalpy.
(ii) HF, HCl, HBr, HI - increasing acid strength.
(iii) NH3, PH3, AsH3, SbH3, BiH3- increasing base strength.
- Q:-
Describe the preparation of potassium permanganate. How does the acidifiedpermanganate solution react with
(i) iron
(II) ions
(ii) SO2 and
(iii) oxalic acid?
Write the ionic equations for the reactions.
- Q:-
A sample of drinking water was found to be severely contaminated with chloroform (CHCl3) supposed to be a carcinogen. The level of contamination was 15 ppm (by mass):
(i) express this in percent by mass
(ii) determine the molality of chloroform in the water sample.
- Q:-
If the solubility product of CuS is 6 x 10-16, calculate the maximum molarity of CuS in aqueous solution.
- Q:-
Boiling point of water at 750 mm Hg is 99.63°C. How much sucrose is to be added to 500 g of water such that it boils at 100°C.Molal elevation constant for water is 0.52 K kg mol-1.
- Q:-
Out of C and CO, which is a better reducing agent for ZnO ?
2 Comment(s) on this Question
the detergent in water
Example sir..
- All Chapters Of Class 12 Chemistry
- All Subjects Of Class 12
