Class 12 Chemistry - Chapter General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements NCERT Solutions | Giving examples, differentiate between &
Giving examples, differentiate between 'roasting' and 'calcination'.
Roasting is the process of converting sulphide ores to oxides by heating the ores in a regular supply of air at a temperature below the melting point of the metal. For example, sulphide ores of Zn, Pb, and Cu are converted to their respective oxides by this process.

On the other hand, calcination is the process of converting hydroxide and carbonate ores to oxides by heating the ores either in the absence or in a limited supply of air at a temperature below the melting point of the metal. This process causes the escaping of volatile matter leaving behind the metal oxide. For example, hydroxide of Fe, carbonates of Zn, Ca, Mg are converted to their respective oxides by this process.
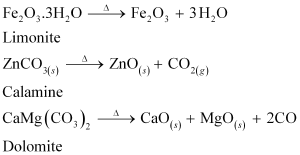
More Questions From Class 12 Chemistry - Chapter General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Q:-
What is the significance of leaching in the extraction of aluminium?
- Q:-
Write down the reactions taking place in different zones in the blast furnace during the extraction of iron.
- Q:-
Copper can be extracted by hydrometallurgy but not zinc. Explain.
- Q:-
Outline the principles of refining of metals by the following methods:
(i) Zone refining
(ii) Electrolytic refining
(iii) Vapour phase refining
- Q:-
Name the common elements present in the anode mud in electrolytic refining of copper. Why are they so present ?
- Q:-
The reaction,
Cr2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Cr (ΔGo = -421kJ)
is thermodynamically feasible as is apparent from the Gibbs energy value. Why does it not take place at room temperature?
- Q:-
How can you separate alumina from silica in bauxite ore associated with silica? Give equations, if any.
- Q:-
Why is the extraction of copper from pyrites more difficult than that from its oxide ore through reduction?
- Q:-
Write chemical reactions taking place in the extraction of zinc from zinc blende.
- Q:-
Describe a method for refining nickel.
Popular Questions of Class 12 Chemistry
- Q:-
For the reaction R → P, the concentration of a reactant changes from 0.03 M to 0.02 M in 25 minutes. Calculate the average rate of reaction using units of time both in minutes and seconds.
- Q:-
Write the formulas for the following coordination compounds:
(i) Tetraamminediaquacobalt (III) chloride
(ii) Potassium tetracyanonickelate(II)
(iii) Tris(ethane-1,2-diamine) chromium(III) chloride
(iv) Amminebromidochloridonitrito-N-platinate(II)
(v) Dichloridobis(ethane-1,2-diamine)platinum(IV) nitrate
(vi) Iron(III) hexacyanoferrate(II)
- Q:-
(i) Write structures of different isomeric amines corresponding to the molecular formula, C4H11N
(ii) Write IUPAC names of all the isomers.
(iii) What type of isomerism is exhibited by different pairs of amines?
- Q:-
Why are solids rigid?
- Q:-
Write any two characteristics of Chemisorption.
- Q:-
Write the structures of the following compounds.
(i) α-Methoxypropionaldehyde
(ii) 3-Hydroxybutanal
(iii) 2-Hydroxycyclopentane carbaldehyde
(iv) 4-Oxopentanal
(v) Di-sec-butyl ketone
(vi) 4-Fluoroacetophenone
- Q:-
Why are pentahalides more covalent than trihalides?
- Q:-
Silver atom has completely filled d orbitals (4d10) in its ground state. How can you say that it is a transition element?
- Q:-
Glucose or sucrose are soluble in water but cyclohexane or benzene (simple six membered ring compounds) are insoluble in water. Explain.
- Q:-
Write structures of the following compounds:
(i) 2-Chloro-3-methylpentane
(ii) 1-Chloro-4-ethylcyclohexane
(iii) 4-tert. Butyl-3-iodoheptane
(iv) 1,4-Dibromobut-2-ene
(v) 1-Bromo-4-sec. butyl-2-methylbenzene
Recently Viewed Questions of Class 12 Chemistry
- Q:-
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points.
CH3CHO, CH3CH2OH, CH3OCH3, CH3CH2CH3
- Q:-
Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system of nomenclature:
(i) CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH2CHO
(ii) CH3CH2COCH(C2H5)CH2CH2Cl
(iii) CH3CH=CHCHO
(iv) CH3COCH2COCH3
(v) CH3CH(CH3)CH2C(CH3)2COCH3
(vi) (CH3)3CCH2COOH
(vii) OHCC6H4CHO-p
- Q:-
Write structural formulas and names of four possible aldol condensation products from propanal and butanal. In each case, indicate which aldehyde acts as nucleophile and which as electrophile.
- Q:-
Complete each synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or products
(i)
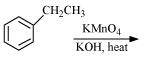
(ii)

(iii)

(iv)

(v)

(vi)
- Q:-
Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than carboxylate ion, carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol. Why?
- Q:-
Calculate the osmotic pressure in pascals exerted by a solution prepared by dissolving 1.0 g of polymer of molar mass 185,000 in 450 mL of water at 37°C.
- Q:-
Write the structures of products of the following reactions;
(i)

(ii)

(iii)

(iv)

- Q:-
Predict the products of the following reactions:
(i)

(ii)

(iii)

(iv)

- Q:-
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds:
(i) PhCH2CH2COOH (ii) (CH3)2C=CHCOOH
(iii)
 (iv)
(iv) 
- Q:-
What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of the reaction in each case.
(i) Cyanohydrin (ii) Acetal
(iii) Semicarbazone
(iv) Aldol
(v) Hemiacetal
(vi) Oxime
(vii) Ketal
(vii) Imine
(ix) 2,4-DNP-derivative
(x) Schiff's base
- All Chapters Of Class 12 Chemistry
- All Subjects Of Class 12
