Class 12 Accountancy - Company Accounts and Analysis of Financial Statements - Chapter Analysis of Financial Statement NCERT Solutions | Explain how common size statements are p
Explain how common size statements are prepared giving an example.
Common size statements can be classified into two broad categories
(i) Common Size Income Statements
(ii) Common Size Balance Sheet
Common Size Statement is prepared in a columnar form for analysis. In a Common Size Statement, each item of the financial statements is compared to a common item. The analyses based on these statements are commonly known as Vertical Analysis. The following are the columns prepared in a Common Size Statement
(a) Particulars Column:This column shows the various financial items under their respective heads.
(b) Amount Columns :These columns depict the amount of each item, sub-totals and the gross total of a particular year.
(c) Percentage or Ratio Columns :These columns show the proportion of each item to the common item either in terms of percentage or ratio. The Common Size Statements can be presented in the following two ways. Method 1 Percentage column is shown beside the amount column of the year to which percentage column belongs.
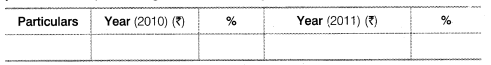
Method 2 Amount columns are shown first and their percentage columns are shown after the amount columns.

Example :From the following information provided by Alfa Limited Prepare the Common Size Statements.
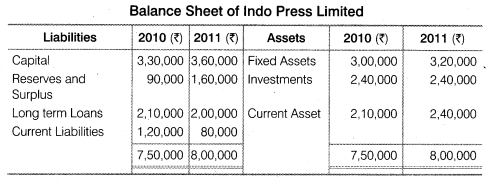
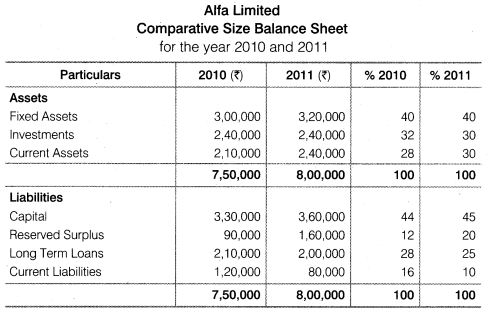
More Questions From Class 12 Accountancy - Company Accounts and Analysis of Financial Statements - Chapter Analysis of Financial Statement
- Q:-
Explain the usefulness of trend percentages in interpretation of financial performance of a company.
- Q:-
What do you understand by analysis and interpretation of financial statements? Discuss its importance.
- Q:-
Describe the different techniques of financial analysis and explain the limitations of financial analysis.
- Q:-
What is the importance of comparative statements? Illustrate youranswer with particular reference to comparative income statement.
- Q:-
What do you mean by Common Size Statements?
- Q:-
State the meaning of Analysis and Interpretation.
- Q:-
List the techniques of Financial Statement Analysis.
- Q:-
What are Comparative Financial Statements?
- Q:-
State the importance of Financial Analysis?
- Q:-
Distinguish between Vertical and Horizontal Analysis of financial data.
Popular Questions of Class 12 Accountancy - Company Accounts and Analysis of Financial Statements
- Q:- What is meant by a Debenture?
- Q:-
What do you mean by Ratio Analysis?
- Q:-
State the meaning of financial statement analysis?
- Q:-
What does a Bearer Debenture mean?
- Q:-
What are various types of ratios?
- Q:-
What are limitations of financial statement analysis?
- Q:-
State the meaning of ‘Debentures issued as a collateral security’.
- Q:-
What relationships will be established to study?
(a) Inventory Turnover (b) Debtor Turnover
(c) Payables Turnover (d) Working Capital Turnover - Q:-
List any three objectives of analysing financial statements?
- Q:-
What is meant by ‘Issue of debentures for consideration other than cash’?
Recently Viewed Questions of Class 12 Accountancy - Company Accounts and Analysis of Financial Statements
- Q:-
‘Financial statements reflect a combination of recorded facts, accounting
conventions and personal judgements’ discuss. - Q:-
Explain the limitations of financial statements.
- Q:-
Explain the nature of the financial statements.
- Q:-
Can the company purchase its own debentures?
- Q:-
Explain the different types of debentures?
- Q:-
What is meant by redemption of debentures?
- Q:-
What is discount on issue of debentures?
- Q:-
What is ‘Capital Reserve’?
- Q:-
Prepare the format of balance sheet and explain the various elements of balance sheet.
- Q:-
What are various types of ratios?
- All Chapters Of Class 12 Accountancy - Company Accounts and Analysis of Financial Statements
- All Subjects Of Class 12
