Question 3: What are important profitability ratios? How are these worked out?
Answer:
Profitability Ratios Profitability ratios measure the results of business operations or overall performance and effectiveness of the firm. Some of the most Important and popular profitability ratios are as under
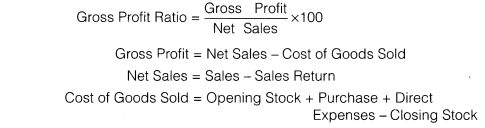
Gross Profit Ratio: Gross Profit Ratio (GP ratio) is the ratio of gross profit to net sales expressed as a percentage. It expresses the relationship between gross profit and sales. The basic components for the calculation of gross profit ratio are gross profit and net sales. Net sales mean sales minus sales returns.
Gross profit would be the difference between net sales and cost of goods sold. Cost of goods sold in the case of a trading concern would be equal to opening stock plus purchase, minus closing stock plus all direct expenses relating to purchases. In the case of manufacturing concern, it would be equal to the sum of the cost of raw materials, wages, direct expenses and all manufacturing expenses. In other words, generally the expenses charged to profit and loss account or operating expenses are excluded from the calculation of cost of goods sold.
Following formula is used to calculate gross profit ratios
Net Profit Ratio :Net Profit Ratio is the ratio of net profit to net sales. It is expressed as percentage. The two basic components of the net profit ratio are the net profit and sales. The net profits are obtained after deducting income-tax and, generally, non-operating expenses and incomes are excluded from the net profits for calculating this ratio. Thus, incomes such as interest on investments outside the business, profit on sales of fixed assets and losses on sales of fixed assets, etc are excluded.

Operating Profit Ratio :Operating Profit Ratio is the ratio of operating profit to net sales. There are many non operating expenses and incomes included in the profit and loss account which has nothing to do with the operations of the business such as loss by fire, loss by theft etc. On the other had in credit side of the P&L account, there are so many incomes
which can be considered as operating incomes such as dividend, bank interest, rent etc. In this way net profit ratio will not tell the truth about the profit of the organisation. Hence operating profit ratio will be helpful in that case. The formula for calculating operating ratio is as follows

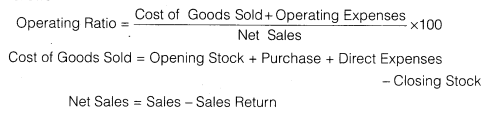
Operating Ratio :Operating ratio is the ratio of cost of goods sold plus operating expenses to net sales. It is generally expressed in percentage, Operating ratio measures the cost of operations per dollar of sales. This is closely related to the ratio of operating profit to net sales. The two basic components for the calculation of operating ratio are operating cost (cost of goods sold plus operating expenses) and net sales. Operating expenses normally include (a) administrative and office expenses and (b) selling and distribution expenses. The formula for calculating the operating ratio is as follows





Add Comment