Class 12 Accountancy - Company Accounts and Analysis of Financial Statements - Chapter Accounting Ratios NCERT Solutions | What relationships will be established t
What relationships will be established to study?
(a) Inventory Turnover (b) Debtor Turnover
(c) Payables Turnover (d) Working Capital Turnover
(a) Inventory Turnover Ratio: This ratio is a relationship between the cost of goods sold during a particular period of time and the cost of average inventory during a particular period. It is expressed in number of times. Stock turnover ratio/inventory turnover ratio indicates the number of time the stock has been turned over during the period and evaluates the efficiency with which a firm is able to manage its inventory. This ratio indicates whether investment in stock is within proper limit or not. The ratio is calculated by dividing the cost of goods sold by the amount of average stock at cost. The formula for calculating inventory turnover ratio is as follows
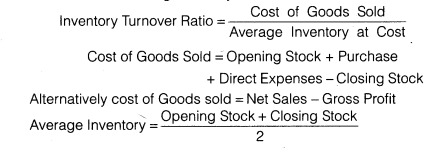
(b)Debtor Turnover Ratio :Debtor turnover ratio or accounts receivable turnover ratio indicates the velocity of debt collection of a firm. In simple words it indicates the number of times average debtors (receivable) are turned over during a year. The formula for calculating Debtors turnover ratio is as follows

(c)Creditors/Payables Turnover Ratio :It compares creditors with the total credit purchases. It signifies the credit period enjoyed by the firm in paying creditors. Accounts payable include both sundry creditors and bills payable. Same as debtor’s turnover ratio, creditor’s turnover ratio can be calculated in two forms, creditors’ turnover ratio and average payment period. The following formula is used to calculate the creditors Turnover Ratio

(d)Working Capital Turnover Ratio Working capital turnover ratio indicates the velocity of the utilization of net working capital. This ratio represents the number of times the working capital is turned over in a year and is calculated as follows
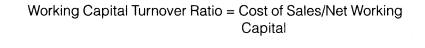
More Questions From Class 12 Accountancy - Company Accounts and Analysis of Financial Statements - Chapter Accounting Ratios
- Q:-
The current ratio provides a better measure of overall liquidity only when a
firm’s inventory cannot easily be converted into cash. If inventory is liquid, the
quick ratio is a preferred measure of overall liquidity. Explain. - Q:-
The liquidity of a business firm is measured by its ability to satisfy itslong-
term obligations as they become due. What are the ratios used forthis purpose? - Q:-
What are liquidity ratios? Discuss the importance of current and liquid ratio.
- Q:-
What do you mean by Ratio Analysis?
- Q:-
What are various types of ratios?
- Q:-
How would you study the Solvency position of the firm?
- Q:-
The average age of inventory is viewed as the average length of time inventory is held by the firm or as the average number of days’ sales in inventory. Why?
- Q:-
What are important profitability ratios? How are these worked out?
Popular Questions of Class 12 Accountancy - Company Accounts and Analysis of Financial Statements
- Q:- What is meant by a Debenture?
- Q:-
List the techniques of Financial Statement Analysis.
- Q:-
State the meaning of financial statement analysis?
- Q:-
What does a Bearer Debenture mean?
- Q:-
Distinguish between Vertical and Horizontal Analysis of financial data.
- Q:-
What are limitations of financial statement analysis?
- Q:-
State the meaning of ‘Debentures issued as a collateral security’.
- Q:-
State the meaning of Analysis and Interpretation.
- Q:-
List any three objectives of analysing financial statements?
- Q:-
What is meant by ‘Issue of debentures for consideration other than cash’?
Recently Viewed Questions of Class 12 Accountancy - Company Accounts and Analysis of Financial Statements
- Q:-
How debentures are different from shares? Give two points.
- Q:-
What is meant by redemption of debentures by conversion?
- Q:-
Describe the steps for creating Sinking Fund for redemption of debentures.
- Q:-
Prepare the format of balance sheet and explain the various elements of balance sheet.
- Q:-
What is meant by ‘Redemption out of Capital?
- Q:-
State the importance of financial statements to
(i) shareholders
(ii) creditors
(iii) government
(iv) investors - Q:-
How would you deal with ‘Premium on Redemption of Debentures?
- Q:-
What is meant by conversion of debentures? Describe the method of such a conversion.
- Q:-
Differentiate between redemption of debentures out of capital and out of profits.
- Q:-
Name the head under which ‘discount on issue of debentures’ appears in the balance sheet of a company.
- All Chapters Of Class 12 Accountancy - Company Accounts and Analysis of Financial Statements
- All Subjects Of Class 12
