About ISRO: The Indian Space Research Organization is the premiere space agency of the Government of India. It was established in 1969 and is administered by the Department of Space of the Indian government.
The Indian Space Research Organization is the sixth largest government run space agency in the world and stands in line with the other leaders of space research and development such as NASA, RKA, ESA, CNSA and JAXA. Early Development.
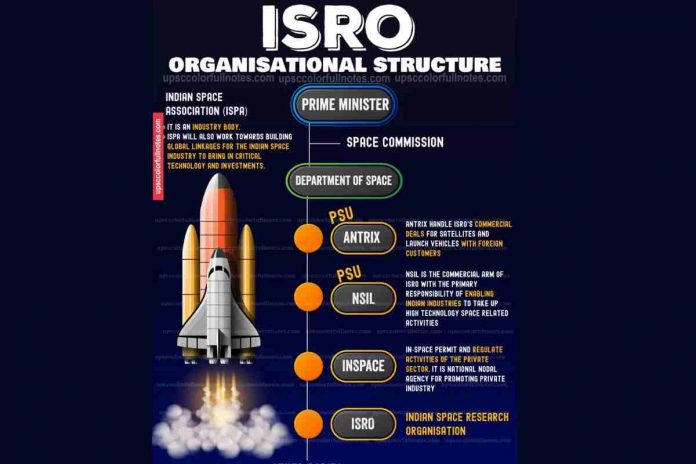
Historical Development About ISRO
ISRO’s roots trace back to 1962 with the formation of the Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) under Dr. Vikram Sarabhai, often regarded as the father of the Indian space program. In 1969, INCOSPAR evolved into ISRO, aiming to leverage space technology for societal and developmental benefits.
ISRO’s predecessor was the Indian National Committee for Space Research. The organization’s first venture was the Aryabhatta which was indigenously developed and launched by the Soviet Union in 1975. ISRO later achieved a significant milestone by launching Rohini in 1980 using its own SLV-3 (Satellite Launch Vehicle).
Subsequently, the organization developed two launch vehicles-the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), which could place satellites in a polar orbit, and Geostationary Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV), which could introduce satellites in a geostationary orbit. Contributions and Roles.
In 2008, the ISRO launched its most ambitious project so far-the Chandrayaan-I, which was the organization’s first lunar probe.
Leadership History: Visionaries Behind ISRO
ISRO owes its foundation and growth to visionary leaders who transformed India’s space dreams into reality:
- Dr. Vikram Sarabhai, the founder of ISRO, is often referred to as the “Father of the Indian Space Program.” His foresight established India’s space program as a tool for national development.
- Dr. APJ Abdul Kalam, a pioneering scientist, played a key role in the development of the SLV-3 launch vehicle and India’s ballistic missile program. His leadership in integrating space technology into defense systems earned him the title of the “Missile Man of India.”
- Dr. K. Sivan and Dr. S. Somnath are among the contemporary leaders steering ISRO towards global recognition, with a focus on cutting-edge technology and collaborative advancements.
Budget and Funding: A Model of Cost-Effectiveness
ISRO has consistently demonstrated how groundbreaking achievements can be accomplished within limited budgets.
- The Mars Orbiter Mission (Mangalyaan), launched in 2013, cost just $74 million, making it one of the most economical Mars missions in history.
- ISRO’s ability to optimize resources has drawn global admiration, showcasing India’s ingenuity in achieving high-tech solutions at a fraction of the cost compared to agencies like NASA and ESA.
Key Achievements and Contributions
ISRO has developed a robust infrastructure of satellites and launch vehicles, achieving self-reliance in space technology.
1. Satellite Development
ISRO has developed an extensive network of satellites serving diverse purposes:
- INSAT (Indian National Satellite System): A series of satellites for telecommunications, television broadcasting, and meteorology.
- IRS (Indian Remote Sensing Satellites): Used for agriculture, forestry, water resource management, and urban planning.
2. Launch Vehicles
- PSLV (Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle): Known for its versatility and reliability, it has launched satellites into polar and sun-synchronous orbits.
- GSLV (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle): Designed to place satellites into geostationary orbit, with an advanced version (GSLV Mk III) capable of carrying heavier payloads.
3. Iconic Missions
- Chandrayaan-I (2008): India’s first lunar probe, which discovered water molecules on the Moon.
- Mangalyaan (2013): The Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), making India the first country to reach Mars orbit in its maiden attempt.
- Chandrayaan-3 (2023): A historic soft landing on the lunar south pole, showcasing India’s technological prowess.
4. Contributions to Society
- Telecommunication and Broadcasting: ISRO’s satellites power one of the world’s largest satellite communication networks.
- Disaster Management: Its remote sensing satellites aid in predicting natural disasters, agricultural monitoring, and urban planning.
- Education and Healthcare: Satellite-based telemedicine and distance education have transformed rural healthcare and education accessibility.
5. Defense Applications
ISRO’s technology has bolstered India’s defense capabilities. The Agni missile series, derived from SLV-3, exemplifies ISRO’s contribution to defense in collaboration with DRDO.
6. Commercial Achievements: Expanding Horizons
ISRO has emerged as a leader in the commercial satellite launch market through its Antrix Corporation, the commercial arm of ISRO, and NewSpace India Limited (NSIL).
- Foreign Satellite Launches: ISRO has successfully launched over 300 satellites from 33 countries, strengthening its reputation in the global satellite market.
- PSLV-C37 Mission: In 2017, ISRO set a world record by launching 104 satellites in a single mission, showcasing its reliability and technical prowess.
- The GSAT series and collaboration with private clients have further solidified ISRO’s commercial success.
7. Collaborations with Indian Space Startups
Recognizing the potential of private space ventures, ISRO has embraced partnerships with Indian startups to foster innovation.
- Skyroot Aerospace: This Hyderabad-based startup, with ISRO’s support, launched India’s first privately developed rocket, Vikram-S, in 2022.
- Agnikul Cosmos: ISRO is collaborating with Agnikul for the development of 3D-printed rocket engines and low-cost satellite launch systems.
- The Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center (IN-SPACe) serves as a nodal agency facilitating public-private partnerships in the space sector, bolstering India’s space ecosystem.
Role Of Indian Science and Research Organization
The Indian Science and Research Organization plays a major role in managing the logistics in various fields of administration, management and industries. The satellite communication network used by India is one of the largest networks in the world and is employed in fields such as land management, natural disaster forecasting, weather forecasting, water resources management, administrative services, radio networking etc.
Furthermore, the Indian satellite and launch vehicles have also found use as spin off products that could be used in the military. The medium range missile Agni was drawn from the SLV-3. The missile was made through the collaborative efforts of resources and technology from ISRO. Former President of India, Dr APJ Abdul Kalam was the head of the project and designed the Agni missile using the SLV-3’s technology.
There are many universities in the country that use satellite services for educational purposes. Furthermore, satellite service has played a pivotal role in the implementation and success of telemedicine.
ISRO’s Global Impact
ISRO’s cost-effective approach has made it a preferred partner for international space missions. The Antrix Corporation, ISRO’s commercial arm, facilitates satellite launches for international clients, contributing to its global reputation.
Future Plans of ISRO
The Indian Science and Research Organization plans to send manned missions to space, take further steps at lunar exploration and conduct interplanetary missions, besides indigenously developing the GSLV. The ISRO has so far undertaken many domestic and international projects.
ISRO has an ambitious roadmap to advance India’s presence in space exploration:
- Gaganyaan Mission: India’s first manned spaceflight mission, aiming to send astronauts into low Earth orbit.
- Aditya-L1 Mission: A solar observation mission to study the Sun’s corona and other solar activities.
- Lunar Exploration: Chandrayaan-4 and collaborative international lunar exploration missions.
- Interplanetary Missions: Proposals to explore Venus and Jupiter, extending ISRO’s planetary research capabilities.
- Commercial Satellite Launches: Strengthening its position as a cost-effective launch service provider for global clients.
FAQs About ISRO
Q. What is ISRO full form?
Ans. ISRO full form is Indian Space Research Organisation.
Also Read: Unveiling Ancient Secrets Of Indus Valley Civilization