Rice Farming Challenges: Rice, one of the major food grain crops of India, accounts for about 40% of the total food grain production. India exports rice to 130 countries. India is the second largest rice producer in the world after China. But India’s rice yield is less than the world average.
Importance of Rice Farming in India
- Base of Agricultural Economy: Rice is the main source of livelihood for millions of farmers in India. About 67% of the population in India is directly or indirectly dependent on agriculture for income.
- Contribution to Food Security: Rice is the staple food of most of the Indian population.
- Export: Rice is a major export product of India, earning foreign exchange.
- Employment Generation: Rice cultivation, processing and distribution provide employment to crores of people.

Rice Farming Challenges in India – Mindmap
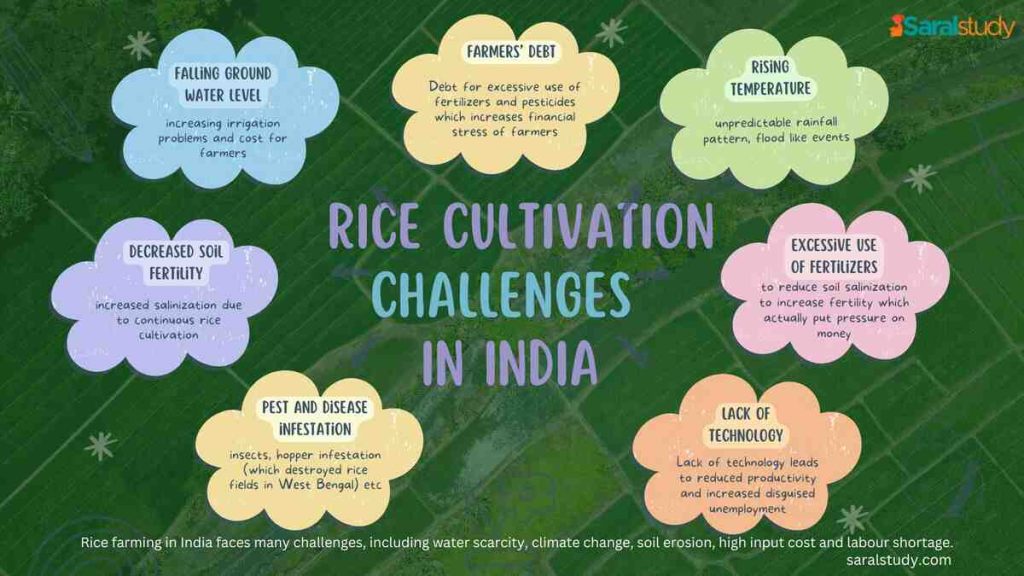
5 Major Reasons for Decrease in Rice Yield in India
The rice production in India is only 2.4 tons per hectare of land, which is 4.7 and 3.6 tons per hectare in China and Brazil respectively. India is far behind its actual potential. There are 5 major reasons for decrease in rice yield in India.
1. Climate and Environmental Challenges
- Falling Water Level: Rice cultivation requires more water, but irrigation problems are increasing due to falling water level.
- Climate Change: Increase in temperature, irregular rainfall, and incidents like floods affect the rice yield.
2. Soil Problems
- Decrease in Soil Fertility: Continuous rice cultivation is reducing the fertility of the soil.
- Salinization: Use of saline water for irrigation and excessive use of fertilizers is increasing the salinization of the soil.
3. Pest and Disease Infestation
- Pest Infestation: Attacks by hoppers and other pests cause heavy damage to crops.
- Diseases: Fungal and bacterial diseases in rice fields affect production.
4. Lack of technology and technique
- Lack of mechanization: Lack of advanced agricultural equipment and technique is reducing the productivity of farmers.
- Lack of training: Small and marginal farmers do not have knowledge of modern agricultural practices.
5. Economic and social factors
- Debt burden: High cost of fertilizers and pesticides puts financial pressure on farmers.
- Disguised unemployment: Due to traditional farming practices, labour is not used properly.
Steps to improve Rice Farming Production in India
Water management technique:
- Water consumption can be reduced by using drip and sprinkler systems.
- Emphasis should be laid on rainwater harvesting and conservation.
Soil quality improvement:
- Soil fertility can be maintained by adopting crop rotation.
- Salinization can be reduced by organic fertilizers and natural methods.
Technological progress:
- Modern machinery and improved seeds should be used.
- Farmers should be trained in advanced agricultural practices. Pest and disease control:
Use organic pesticides:
- Regular monitoring of crops for better management.
Government role:
- Relieve farmers from debt pressure by providing subsidies and financial assistance.
- Insurance schemes and fair price guarantee in the market for small farmers.
Private and public partnership:
Private and government institutions should jointly invest in research and development in the agricultural sector.
Conclusion
Rice cultivation in India is facing many challenges, such as water scarcity, climate change, declining soil fertility, and economic problems. To deal with these problems, it is necessary to adopt sustainable agricultural practices, modern technologies, and supportive policies. Rice cultivation can be made more profitable and sustainable through digitalization of agriculture, strengthening government schemes, and empowerment of farmers.
Also Read: Green Revolution in India

